Heat resistance
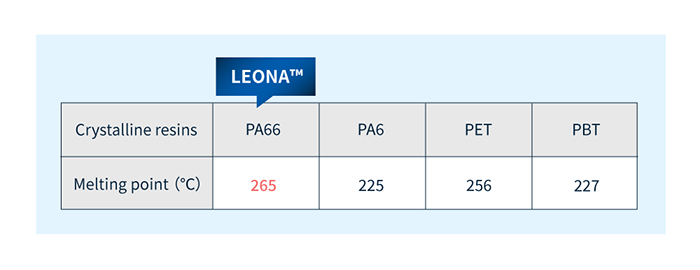
LEONA™ PA66 resins have a high melting point (265°C) in general-purpose engineering plastics and boast excellent heat resistance.
NEW SERVICE!
CAE ServicesFor inquiries regarding SDS and various chemical substance investigations, please make your request through your purchasing route, such as via a trading company.
We appreciate your understanding and cooperation.



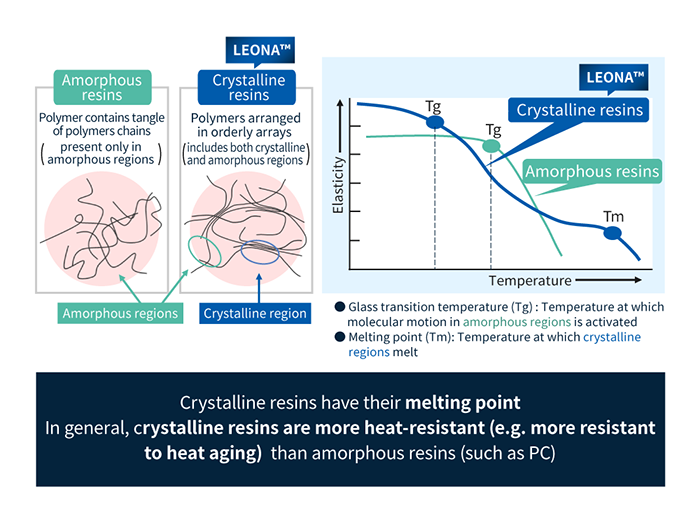
LEONA™ is Asahi Kasei's family of PA66 (polyamide 66, nylon 66) resins.
PA66 is short for polyamide 66—the chemical name—and also known as nylon 66 . PA66 is engineering plastic featuring excellent heat resistance and mechanical strength. PA 66 is crystalline thermoplastic resin.
Asahi Kasei is responsible for every step in the manufacturing process for PA66 polymers in house, starting from intermediates such as acrylonitrile, adiponitrile, hexamethylenediamine, and adipic acid.
We offer a wide range of product grades suitable for many different purposes spanning many industrial sectors—making us both Asia's No. 1 manufacturer* of PA66 resin and the No. 1 manufacturer in the Japanese market*, supplying PA66 resin primarily to Japanese automakers and meeting a broad spectrum of customer needs.
*Source: Based on global market sales volume and Japanese market sales volume from Fuji Keizai's 2023 Engineering Plastics Market Outlook and Global Strategy.

LEONA™ is Asahi Kasei's family of PA66 resins. These products are classified as engineering plastics featuring outstanding heat resistance and mechanical strength
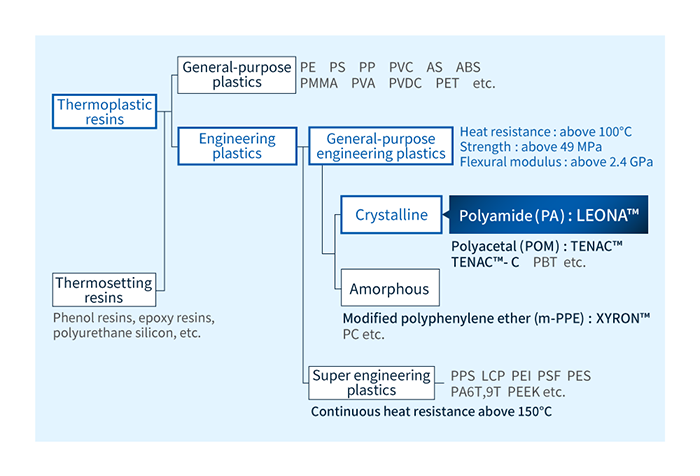
LEONA™ PA66 resin is crystalline thermoplastic, exhibiting a good balance of several key properties, including the following.
LEONA™ PA66 resins have a high melting point (265°C) in general-purpose engineering plastics and boast excellent heat resistance.


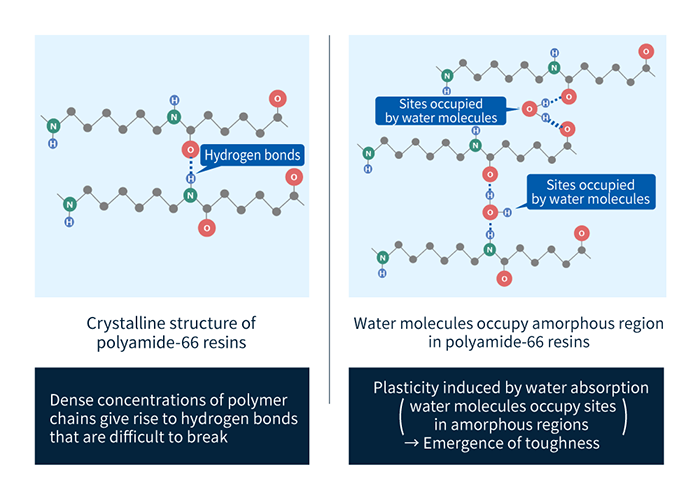
LEONA™ PA66 resins feature excellent strength and rigidity. The high toughness and excellent impact resistance of these materials are valuable features. These properties are derived from the molecular structure of PA66 resins, which feature tightly interwoven polymer chains with hydrogen bonds acting between molecules; the water absorption of these materials allows them to exhibit water-absorption-induced plasticity (with water molecules occupying amorphous sites).
These properties make LEONA™ materials an effective alternative to metals.
LEONA™ PA66 resins feature excellent electrical insulation and tracking resistance. These properties are derived from the absence of benzene rings in the molecular structure of PA66 resins, which are thus resistant to carbonization.
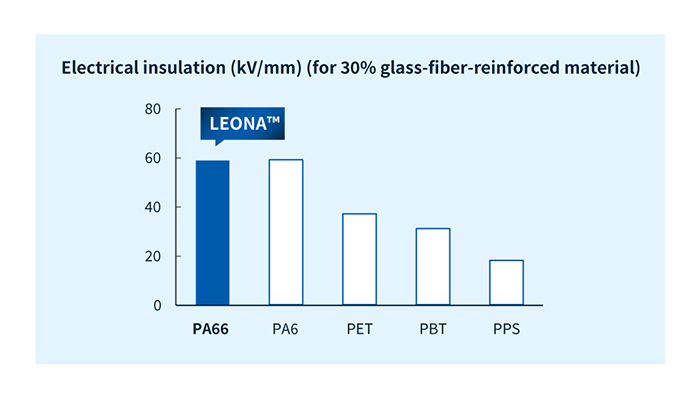
LEONA™ PA66 resins feature excellent resistance to non-acid chemicals, organic solvents, lubricant oils, and similar substances.
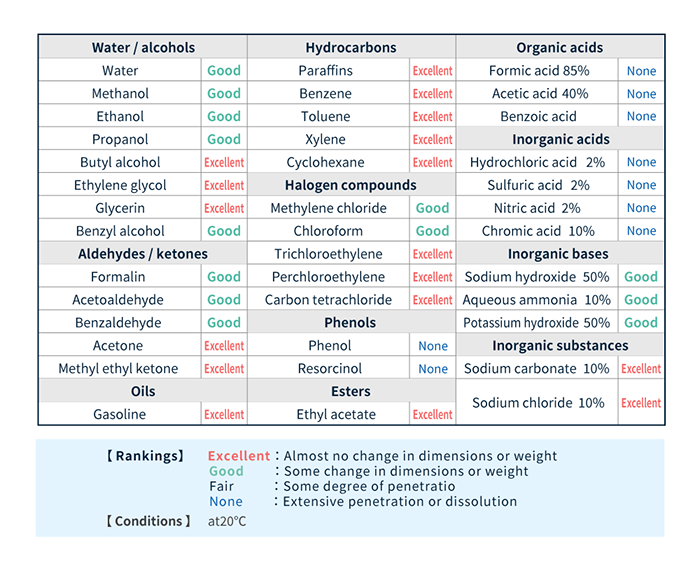
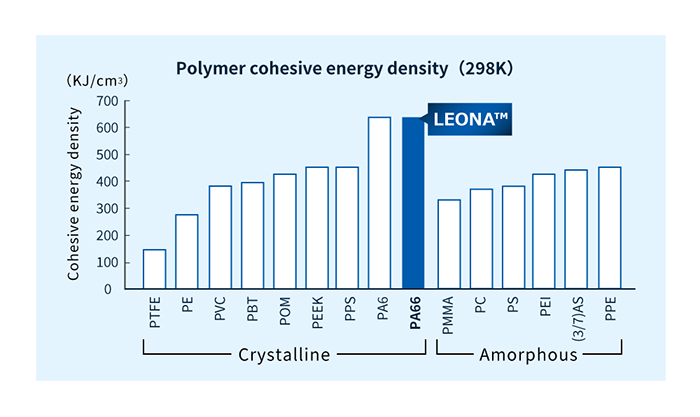
LEONA™ PA66 resins has high intermolecular cohesion and do not become brittle even when compounded with fillers.
The cohesion is defined as the cohesive energy density which is the cohesive energy divided by the molar volume. A comparison among polymers shows that the cohesive energy density of polyamide is much higher than that of other polymers (see figure).
Plastics are often compounded with glass fiber (GF), mineral fillers, and other additives to improve material strength, etc. However, large amounts of such additives can cause brittleness and a drop in strength and impact resistance. Therefore, there is a maximum limit to the amount of fillers added to plastics, and the limit varies depending on the type of plastic.
As mentioned above, polyamide has a high cohesive energy density, so it does not become brittle even when reinforced with a high filler content and can be reinforced with a larger amount of fillers to enhance various performance characteristics.
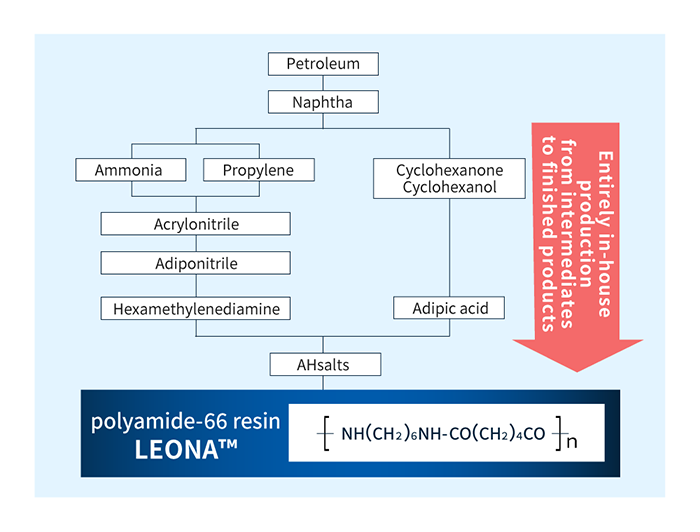
Asahi Kasei is the only manufacturer in Asia producing PA66 resins entirely in-house, from intermediates to finished products. Indeed, we are among a handful of firms worldwide producing our own adiponitrile, from which we make hexamethylenediamine; we also produce adipic acid from cyclohexanol made by our own proprietary method (the cyclohexane method). From these intermediates, we make LEONA™ PA66 resins. Our fully in-house production process minimizes external disruptions to reduce supply instability.
As Asia's No. 1 manufacturer* of PA66 resins and the No. 1 manufacturer in the Japanese market*—supplying resins primarily to Japanese automakers—Asahi Kasei leverages decades of experience to develop a wide range of material grades for the automotive industry and many other industrial sectors for many different purposes. Our extensive lineup of product grades serves a broad variety of customer needs. With 37% of the entire Japanese market, Asahi Kasei is Japan's No. 1 supplier*
*Source: Based on global market sales volume and Japanese market sales volume from Fuji Keizai's 2023 Engineering Plastics Market Outlook and Global Strategy.
With offices in many countries around the world, Asahi Kasei supports our customers on a global basis.
Moreover, our “resin CAE technology” service—Asahi Kasei's in-house design-simulation expertise—is available to support customers in the product design and development stages.
→ Click here for details on Asahi Kasei's technical support


Asahi Kasei is proud to offer an extensive lineup of LEONA™ polyamide resin grades featuring a variety of polyamide resins blended with fillers and other additives.
For the standard PA66 series, we offer standard, heat resistant, glass-fiber (GF) reinforced, low warpage/low wear, impact resistant, high viscosity/fatigue resistant, sliding, and Flame retardance grades.
Beyond the PA66 family, we also offer grades based on PA66/6I—a compound blended with semi-aromatic polyamide 6I—and grades based on 66+6I polymer alloys, as well as grades based on low-water-absorption PA612 and grades based on PA610, which features low water absorption and is derived from plant matter.
As a newly developed material, flame retardants that do not contain halogens or red phosphorus are used, and the PA66+6I flame retardant grade LEONA™ SN series, which has excellent appearance and high strength when absorbing water, etc., is used for unpainted exteriors. PA6+6I grade LEONA™ SU series with excellent moldability and strength is available. We are also developing extrusion grades that can be applied to EV cooling pipes, pipes, and tubes.
Please contact us to ask any questions, discuss any concerns, and request samples.
Please feel free to contact us with any questions about our products or technologies or to request samples.
We will introduce Asahi Kasei 's engineering plastic products and technologies in more detail.
We regularly deliver product and industry information to help you gather information.