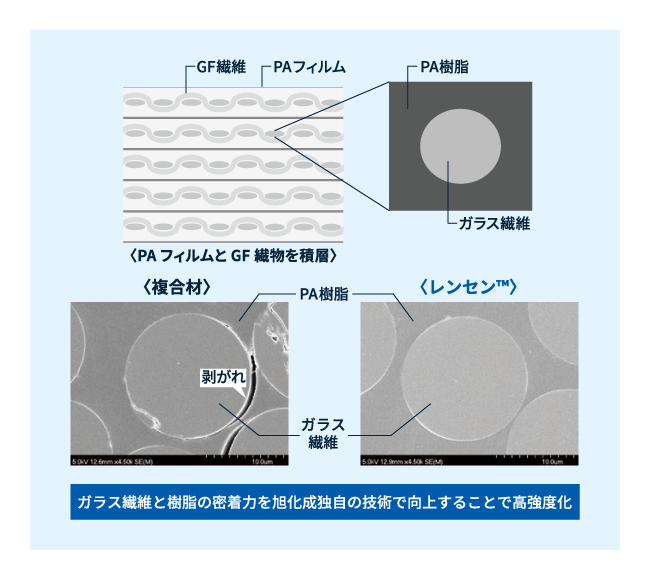
高強度・高剛性
旭化成独自の技術によって、ガラス繊維と樹脂の密着力を向上することで、高強度化を実現しています。
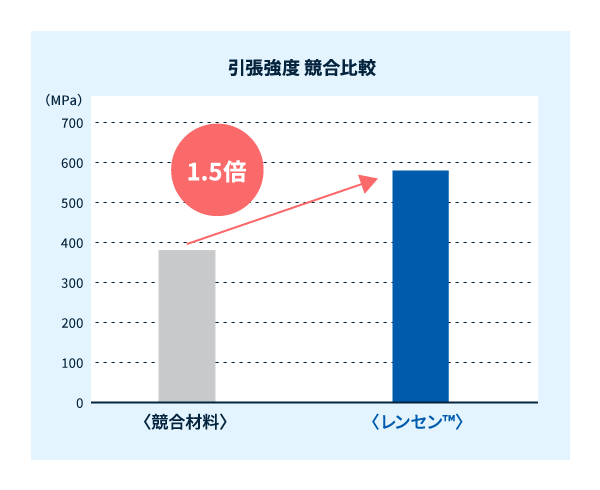
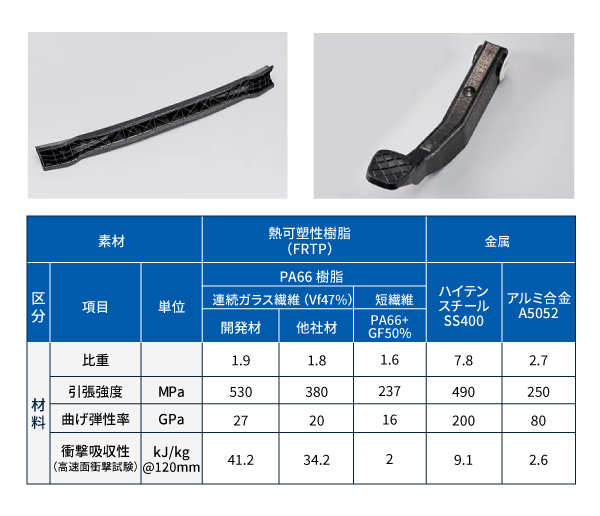
「レンセン™」は、金属に対しても同等以上の引張強度と衝撃吸収性を有する事から、衝突安全性の向上や軽量化効果を得ることが期待でき、信頼性や燃費向上にも貢献できる材料として提案していきます。
樹脂CAE
SDS・各種化学物質調査のお問い合わせは
お取引商社様経由など
購入ルートに沿ってのご依頼をお願いしております。
ご了承とご協力のほどお願いいたします。
「レンセン™」は、連続ガラス繊維の織物とポリアミド66(PA66)のフィルムを積層させた旭化成の連続繊維強化複合材料です。
連続繊維強化複合材料は、ガラス繊維の織物などに熱可塑性樹脂を含浸させて固めた板状の成形材料で、コンポジット材料と言われることもあり、欧州ではオルガノシート、プリプレグ(Prepreg)などとも言われます。
英語ではContinuous Glass Fiber Reinforced thermoplastic の頭文字をとってc-GFRTPと表していますが(最初のcは小文字)、他にもGFRTPやGFRPなどの表記もあります。
連続ガラス繊維の織物とポリアミド66(PA66)のフィルムを積層させたプリプレグ「レンセン™」の特徴、製造方法をご紹介します。
旭化成独自の技術によって、ガラス繊維と樹脂の密着力を向上することで、高強度化を実現しています。
「レンセン™」は、金属に対しても同等以上の引張強度と衝撃吸収性を有する事から、衝突安全性の向上や軽量化効果を得ることが期待でき、信頼性や燃費向上にも貢献できる材料として提案していきます。


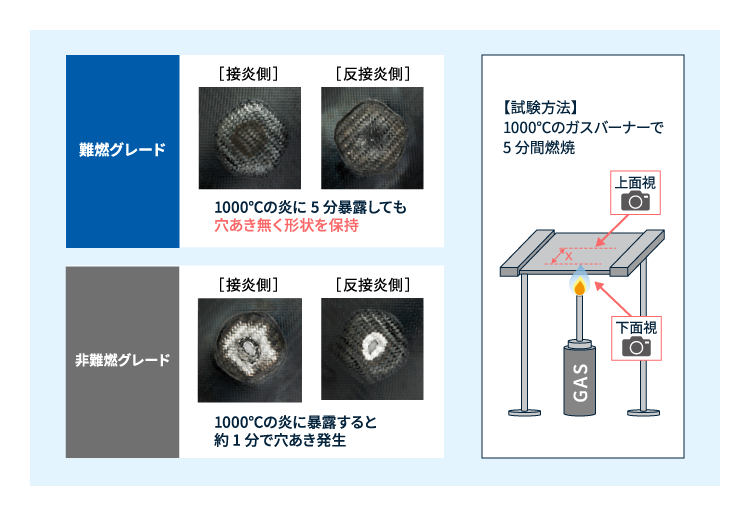
難燃グレードでは、1000℃ 5分のバーナー火あぶり試験で穴あきなし。
例えば、EV/バッテリーの熱暴走時の燃え広がりを遅らせ、乗員の保護に貢献できます。
「レンセン™」は次のように作ります。
また、PA66は熱可塑性樹脂のため、「レンセン™」は同種材による射出成形との複合化が可能です(プレス+射出ハイブリッド成形)。これによりリブやフランジなどの複雑形状が形成でき、部品の剛性向上や周辺部品の統合による部品のコストダウンの可能性があります。
【プリプレグとは】
含浸を英語でインプレグネイション(Impregnation)と言い、製造された板状の成形基材をプリプレグ(Prepreg)やオルガノシート(Organo sheet)と呼びます。
プリプレグを構成する材料には多数の組み合わせがあります。樹脂フィルムにはポリアミドやポリプロピレンのような熱可塑性樹脂のほかに熱硬化性樹脂も使われます。強化繊維にはガラス繊維や炭素繊維などが使われ、繊維の形態には連続した繊維の織物や一方向に揃えたもの(UD)、不連続の繊維による不織布(ランダム)などがあります。
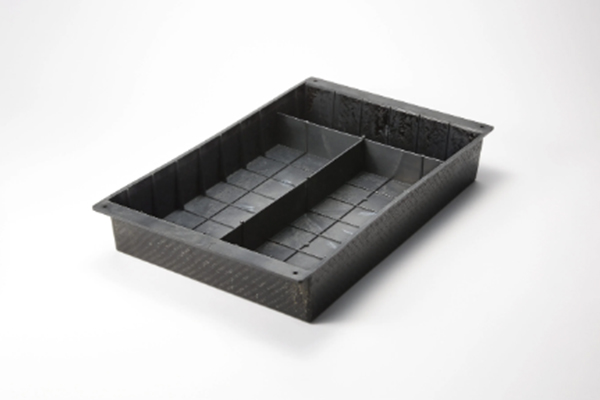
EV車のバッテリーケースには鉄やアルミなどの金属が主に使われ、走行距離延伸のために軽量化が求められる一方、樹脂化検討には電池の連続爆発時に耐えうる高い難燃性とコスト削減が課題になっています。
「レンセン™」は、

バンパービームやブレーキペダル等の部品には、鉄やアルミなどの金属が使用されており、軽量化出来る可能性が多く残されています。
これらの部品には、強度、剛性、衝撃吸収性、耐久性に優れた材料が必要であり、それらの特徴を兼ね揃えた「レンセン™」が適していると考えています。
鉄製バンパービームには曲げ加工や別部品との溶接等の後加工が必要になりますが、本材料で一体成型する事によって軽量化に加え、工程数と部品点数を削減出来る可能性があります。
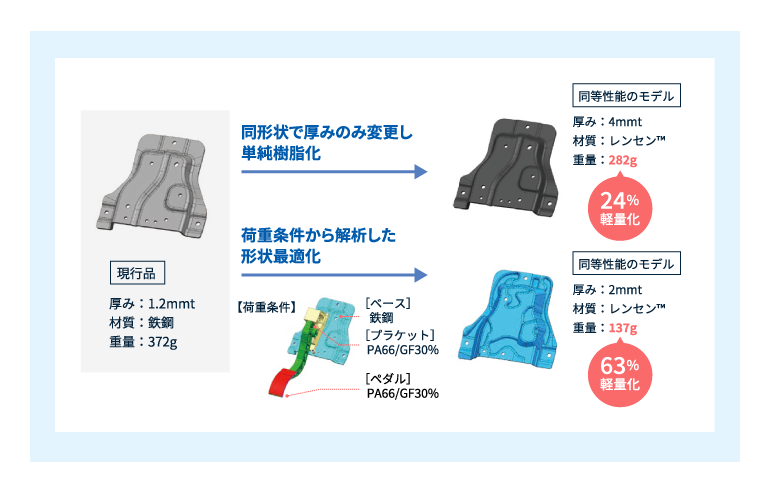
旭化成独自のCAE技術により形状を最適化することで、さらなる軽量化が可能です。
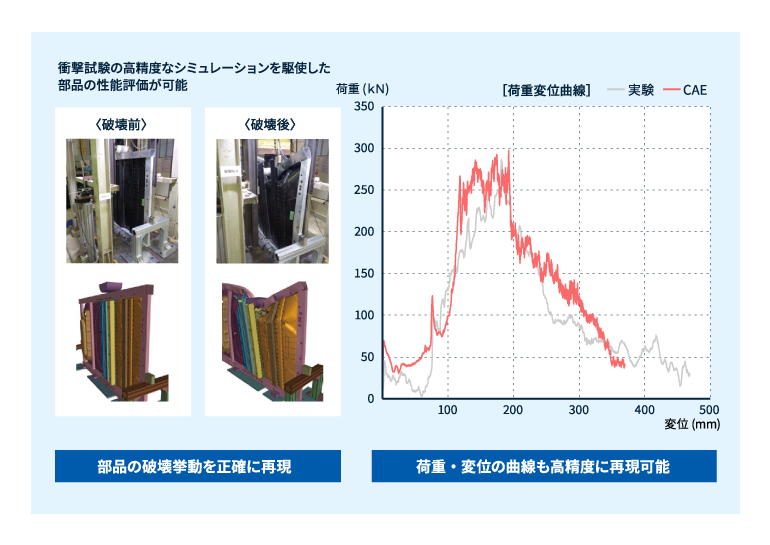
下記バッテリーカバーの側突試験のように衝撃時の破壊挙動と吸収エネルギーを正確に再現します。
レンセン™(c-GFRTP)に関するご質問・ご相談・サンプルのご依頼をお待ちしております。