Technical Information
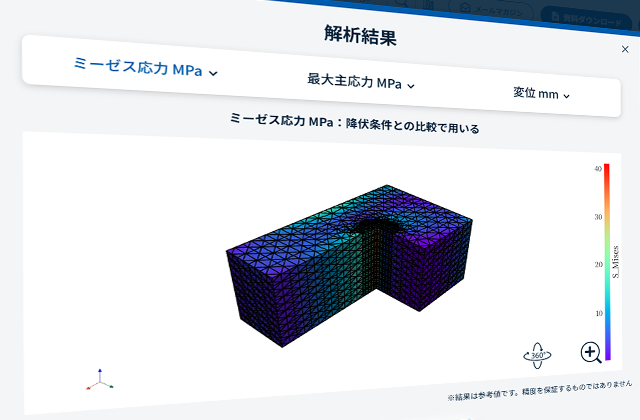
Static structural analysis Details
Properties of resin composites
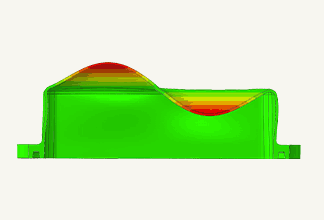
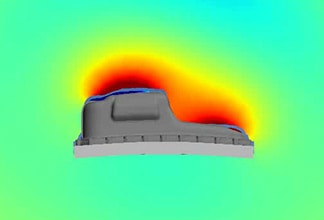
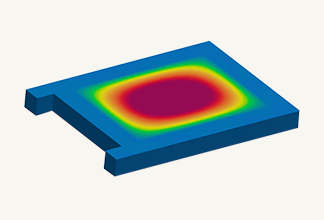
Resin composite materials contain anisotropic glass-fiber as reinforcing materials, and as such have the characteristic that their physical properties vary depending on the degree of glass-fiber orientation after injection molding.
In fact, when dumbbell-shaped test pieces are cut at different angles from a plate test piece created by injection molding and subjected to tensile tests, the stress-strain curves are different.
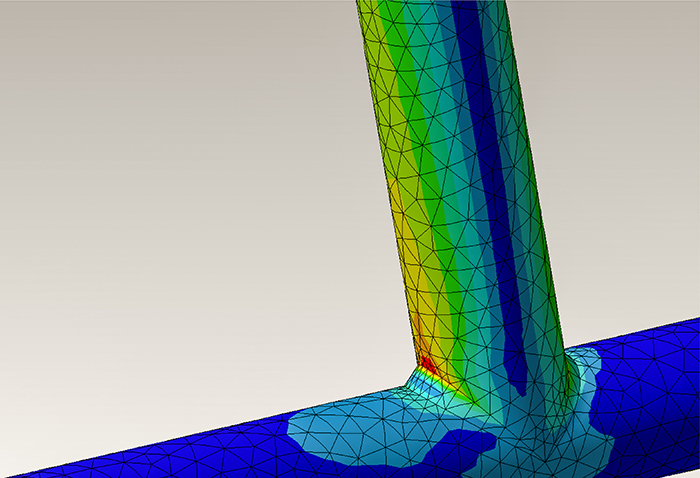
In order to improve the accuracy of structural analysis, Asahi Kasei is working to take fiber orientation into account.
The mechanical properties are strongly influenced by the fiber orientation distribution.
We have improved the accuracy of structural analysis by using data that considers this fiber orientation distribution.
.png)
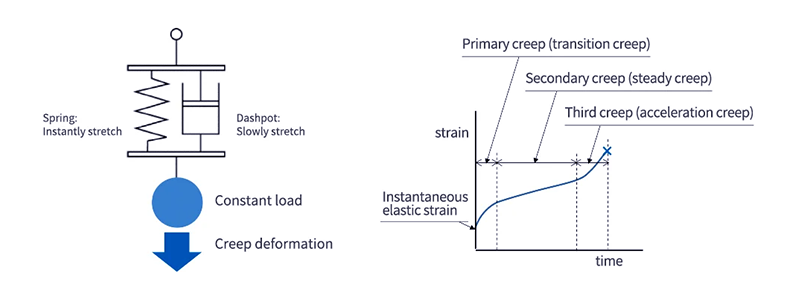
Creep property of plastics
Creep is the phenomenon in which an object slowly deforms over time when a certain load is applied to it.
Resin undergoes creep even at room temperature, and resin creep is divided into three stages, eventually resulting in rupture.
Plastic has three stages of creep.
The primary stage involves significant deformation.
In the secondary stage, it is constantly deformed.
In the tertiary stage, the deformation is accelerated and finally breaks.