Technologies and Products

For inquiries regarding SDS and various chemical substance investigations, please make your request through your purchasing route, such as via a trading company.
We appreciate your understanding and cooperation.
2024.11.13

Technologies and Products
In recent years, the use of composite materials made by laminating fiber-reinforced plastics (FRP), a plastic reinforced with glass-fiber or carbon fiber, and foam has been expanding in order to reduce the weight and increase the stiffness of parts for automobiles, aircraft, and other devices.
Generally, the thicker the component and strength the outermost layer, the greater stiffness. By creating a composite like this, it is possible to increase the thickness using lightweight foam, while placing a strength FRP layer on the surface, making it possible to create a lightweight yet stiffness component.
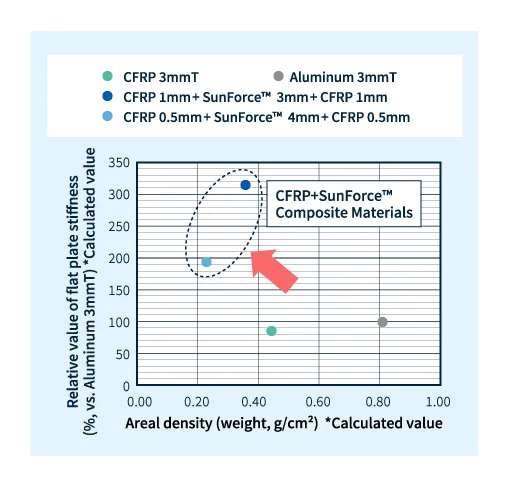 Comparison of plate stiffness between CFRP + SunForce™ composite material and CFRP/aluminum alone (calculated values)
Comparison of plate stiffness between CFRP + SunForce™ composite material and CFRP/aluminum alone (calculated values)
Well-known core materials for composite materials include honeycomb, balsa wood (a type of wood), and foam, but composites made from FRP and foam are attracting attention because they have no anisotropy in strength, are flexible in shape, can be combined without adhesives, and are relatively inexpensive.
However, methods such as the autoclave method, PCM (Prepreg Compression Molding) method, and RTM (Resin Transfer Molding) method, which are known for manufacturing composite materials made from FRP and foam core materials, generally require high heat resistance of over 100°C during the compounding process.
Therefore, the applicable foams are limited, and most of the high-heat-resistant foams are in sheet form, requiring pre-cutting, which leads to high processing costs and poor productivity.
Asahi Kasei proposes composite corematerials using the PCM method to mold the engineering plastic foam beads "SunForce™ " with FRP as one of the composite methods.
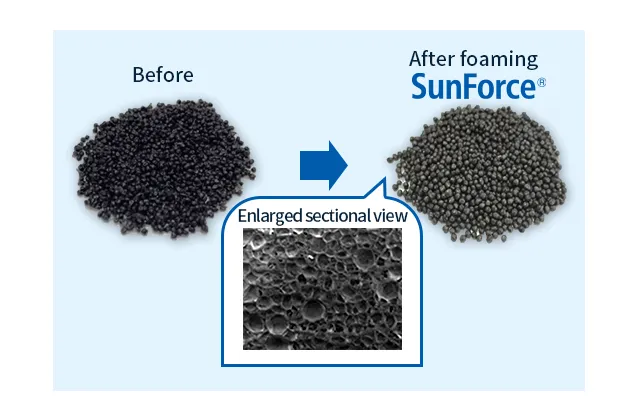
SunForce™ is a foamed bead made from modified PPE resin (modified polyphenylene ether resin), and combines heat resistance, dimensional stability, and low water absorption of modified PPE with the lightweight, heat insulating, and formability of foamed beads.
Additionally, because Sunforce™ is molded through in-mold foaming, it excels in mass production, especially for small to medium-sized parts.

The features of composites made from Sunforce™ and FRP using the PCM method are as follows:
Due to SunForce™'s high heat resistance, it undergoes the PCM process without noticeable defects such as shrinkage, and its in-mold shaping allows the manufacture of FRP composite materials with complex shapes like curved surfaces.
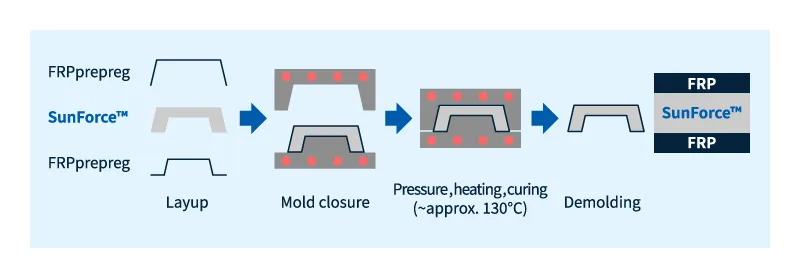 Method of Manufacturing SunForce™ Molds and FRP Composite Materials (PCM Method)
Method of Manufacturing SunForce™ Molds and FRP Composite Materials (PCM Method)
Sunforce™ has advantages in terms of cost and mass production.
Since Sunforce™ is formed by in-mold foaming, no pre-processing such as cutting is unnecessaryTherefore, as shown in the diagram below, it provides significant benefits particularly for applications that require shaping and medium- to high-volume production of FRP composites.
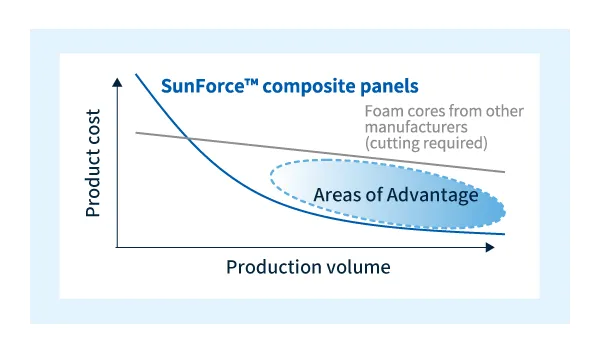 Cost Advantage of SunForce™
Cost Advantage of SunForce™
Sunforce™ can be shaped by in-mold foaming, allowing the production of FRP composites into complex shapes such as curved surfaces.
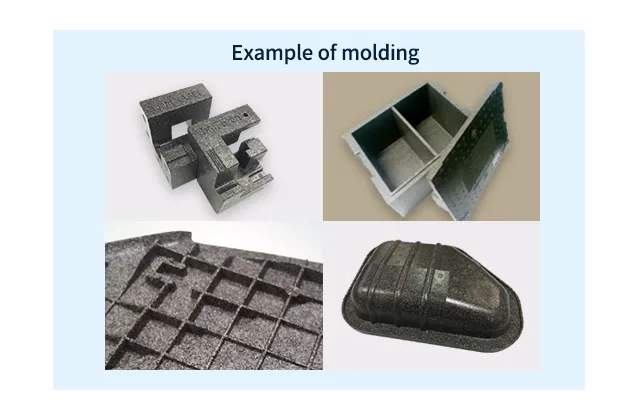
 Examples of Formed SunForce™ Composite Materials
Examples of Formed SunForce™ Composite Materials
Sunforce™ is a foam with a closed-cell structure based on low water-absorption m-PPE resin, offering lower water absorption compared to other foams used in conjunction with FRP.
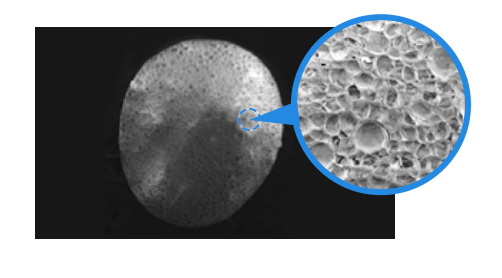 Cross-section of particle foam beads
Cross-section of particle foam beads
SunForce™ is a foamed material based on m-PPE resin, which has low dielectric properties, and therefore has very low dielectric properties. Therefore, when used as a core material for FRP composites, it is possible to achieve very high radio wave permeability while maintaining light weight and stiffness.
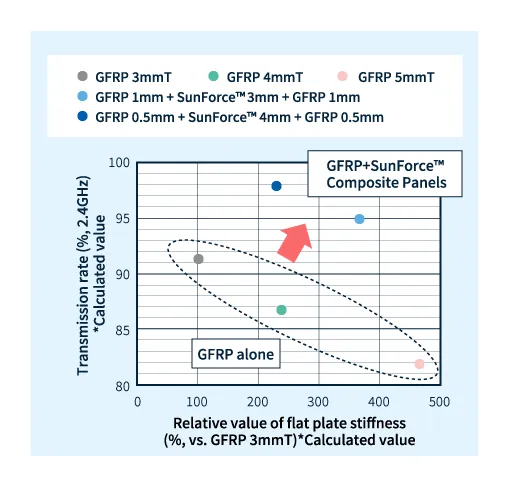 Comparison of radio wave permeability between GFRP + SunForce™ composite material and GFRP alone (calculated values)
Comparison of radio wave permeability between GFRP + SunForce™ composite material and GFRP alone (calculated values)
Furthermore, by controlling the thickness of each layer of SunForce™ and FRP, it is possible to create a composite material with increased transmittance in both the front and oblique directions.
These characteristics make it suitable for applications requiring high-power radio wave transmission and reception (such as base stations, radomes installed in automobiles, airplanes, drones, etc., and wireless power supply covers).
→ サンフォース®の誘電特性・通信機器向けの活用提案の詳細はこちら
As described above, using SunForce™ as a foam core material for FRP composites allows the production of lightweight, high-rigidity, complex-shaped FRP composite materials with high mass productivity.
If you are interested, please contact us.
Please contact us to ask any questions, discuss any concerns, and request samples.
Please feel free to contact us with any questions about our products or technologies or to request samples.
We will introduce Asahi Kasei 's engineering plastic products and technologies in more detail.
We regularly deliver product and industry information to help you gather information.