製品
耐熱性、強度・靭性、絶縁性、耐油性に優れます。自動車部品、電機・電子部品など幅広く採用されています。
樹脂CAE
SDS・各種化学物質調査のお問い合わせは
お取引商社様経由など
購入ルートに沿ってのご依頼をお願いしております。
ご了承とご協力のほどお願いいたします。

自動車業界において、欧州や中国を中心に、全世界的にBEV(Battery Electric Vehicle:電気自動車)化が急速に進んでいます。電気自動車では、エンジンに代わってモーター、バッテリー、インバーターの3点が主要モジュールとなります。
BEVはエンジン車と比較してエネルギー効率が高い一方で、バッテリーに大量のエネルギーを蓄えることは難しく、モーターやバッテリーをできるだけ効率よく使用する必要があります。モーターやバッテリーは使用中に温度上昇しますが、適切な温度に保つことでエネルギー効率が高まり、航続距離を延長することができます。
BEVではこの熱マネジメント(Thermal Management)技術が重要です。従来はバッテリー、パワートレイン、空調(Air Conditioning, A/C)などそれぞれのユニットを個々に管理する分散管理型が大半でしたが、車両全体で熱マネジメントを統合するBEVも出現しています。
旭化成は、バルブ・パイプ・ポンプといった、熱マネジメントシステムを構成する様々な製品向けの材料と技術支援を提案し、バッテリーEVの開発を支援します。
ポリアミド樹脂レオナ™ は強度・剛性、耐熱性、耐薬品性に優れたエンジニアリングプラスチックです。ガラス繊維(GF)のような充填材(フィラー)によって強化することで、強度・剛性、耐久性、寸法安定性を向上することができます。
レオナ™ 14G30は、強度、耐LLC性、レーザー溶着性、レーザー印字性という材料特性をもち、BEVの熱マネジメントシステムのバルブの材料として、採用された実績があります。As one example, LEONA™ 14G30 is a material with a proven track record of successful adoption for valves in thermal management systems. To help our customers take full advantage of the superior physical properties of this material—including its high strength, resistance to long-life coolants, and excellent laser-welding and laser-marking characteristics—Asahi Kasei offers extensive technical support services: our experienced engineers work together with customers to accelerate product development and achieve innovative solutions.
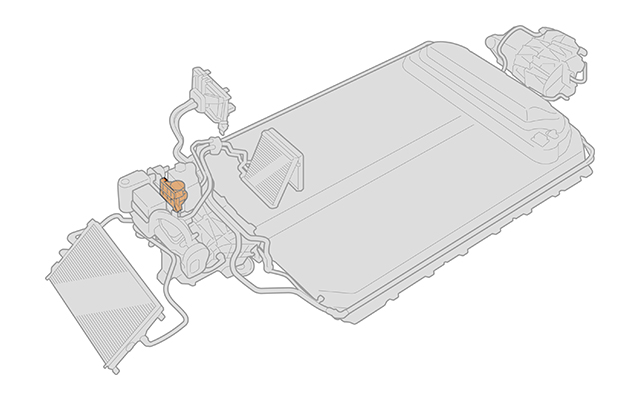
一般的に、アルミニウム合金などの金属や、金属とゴムを組み合わせた材料が用いられるBEVの冷却配管(パイプ)に、エンジニアリングプラスチックを用いることで、部品の一体化による軽量化やコスト低減に貢献できます。
旭化成では、冷却配管(パイプ)の設計の目的に応じて、適した材料と成形方法をご提案します。ここからは、パイプ形状の各種成形方法と、対応する樹脂材料をご紹介します。
WITは、パイプのような中空形状を得るための特殊な射出成形方法です。
溶融樹脂を充填後、表層は固化・中心部はまだ溶融状態というタイミングで、中心部に水を充填し中空構造を作ります。比較的短い(~50cm目安)ものに適していますが、分岐や異形断面・径変更が可能なため、分岐屈曲した冷却パイプに適合します。
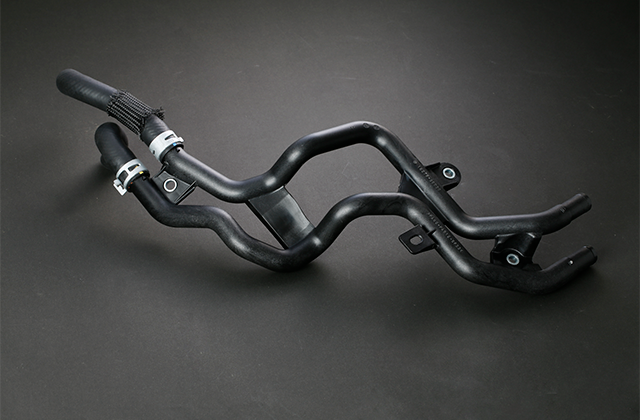

加熱溶融された樹脂を金型(ダイ)から押し出し、一定断面形状を連続的に成形する方法です。
細径で長尺なパイプ・チューブを得ることができます。また、後加工によって自由な配管レイアウトの構築が可能で、バッテリーパックの冷却配管や、ラジエーターとバッテリーパック間あるいはモーター間等のユニット同士を繋ぐパイプ・チューブに適合します。
旭化成は、上記の水冷式熱マネジメントシステムの冷却配管向けに、PA612樹脂レオナ™押出成形グレードをご提案します。
PA612は柔軟性・耐加水分解性・耐熱老化性・耐薬品性などの特徴を持ち、冷却配管に適した材料です。

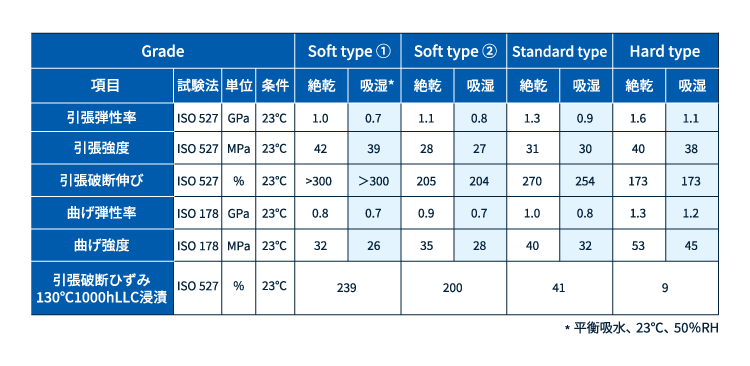
注)これらの物性は定められた試験法に基づいて得られた代表値であり、保証値ではありません。個々の用途に最適なグレードを選ぶ目安としてご参照ください。なお、これらの数値は物性改良のため変更することもあります。試作品は、量産時に物性値が変わる場合があります。
ポリアミド樹脂レオナ™ BG230は、ポリマーの60%が植物由来であるバイオマスプラスチックPA610をベースとした材料です。
PA610はPA66よりも吸水率が低いことから、水に触れる使用環境でも寸法安定性が良く、耐薬品性、耐塩化カルシウム性に優れた材料です。また、レーザー溶着性にも優れており、冷却ポンプの小型化・軽量化に貢献します。
サンフォース®は軽量、断熱性という発泡体ならではの性能に加えて、難燃性(UL-94 V-0)、寸法精度、薄肉成形などの、従来の発泡体を超えた機能を併せ持ったm-PPE(変性ポリフェニレンエーテル)のザイロン™をベースとした発泡体です。
サンフォース®は発泡させている分、樹脂の使用量が少ないため樹脂部を伝わる「伝導」が小さく、高い断熱性を有しています。

バッテリーが低温になると、その出力が大きく低下する事が知られています。 電気自動車や高出力のハイブリッド車では、セルの温度低下を防止するために、SunForce™ヒーター等で加熱して適温に維持する工夫をされている車両もあります。

また、サンフォース®は、発泡体でありながら、難燃性が必要な部分にも使用することができます。
サンフォース®は、ULのプラスチック・部材向け難燃規格「UL-94」にて、非常に高いレベルの難燃性である「V-0」の認定を、発泡ビーズ材料として世界で初めて受けています。また、軽量な発泡体であり、自己消火性があるという特徴から、既にEVの電池パック周辺部品での採用・検討が進んでいます。

旭化成は、金属部品を樹脂化するためのプラスチック用CAE(樹脂CAE)の研究・応用を長年行ってきました。この樹脂CAE技術を駆使して、短期・低コストで高性能な製品開発をサポートします。
例えば、バルブや弁のような部品において金属から樹脂への置き換えを図る場合、強度や剛性の不足、ウエルドラインの強度低下が懸念されます。
この場合、シミュレーション技術を用いて形状やゲート位置を検討し、ウエルドラインの影響を最小限に抑えたり、使用中に破壊や漏れが発生しないように、設計や性能予測を実施します。
